Vitamin D deficiency is a prevalent issue, yet its symptoms can often be subtle and overlooked. This essential nutrient plays a crucial role in the body’s functioning, particularly in bone health, immune support, and even preventing chronic conditions like cancer and heart disease. Below, we’ll discuss the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, its treatment options, and how to boost your vitamin D levels.
What Is Vitamin D and Why Is It Important?
Vitamin D, often referred to as the sunshine vitamin, is a fat-soluble vitamin that the body produces when the skin is exposed to sunlight. It’s vital for various bodily functions, including:
- Bone Health: It helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for bone strength.
- Immune Function: Supports the immune system and may reduce the risk of infections.
- Chronic Disease Prevention: Research suggests it may help protect against several chronic conditions like cancer, type 2 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and heart disease.
However, many people globally suffer from vitamin D deficiency, especially in regions with limited sunlight or in populations with certain health conditions. In the United States, nearly 42% of adults are deficient, with higher rates among Hispanic and African American populations.
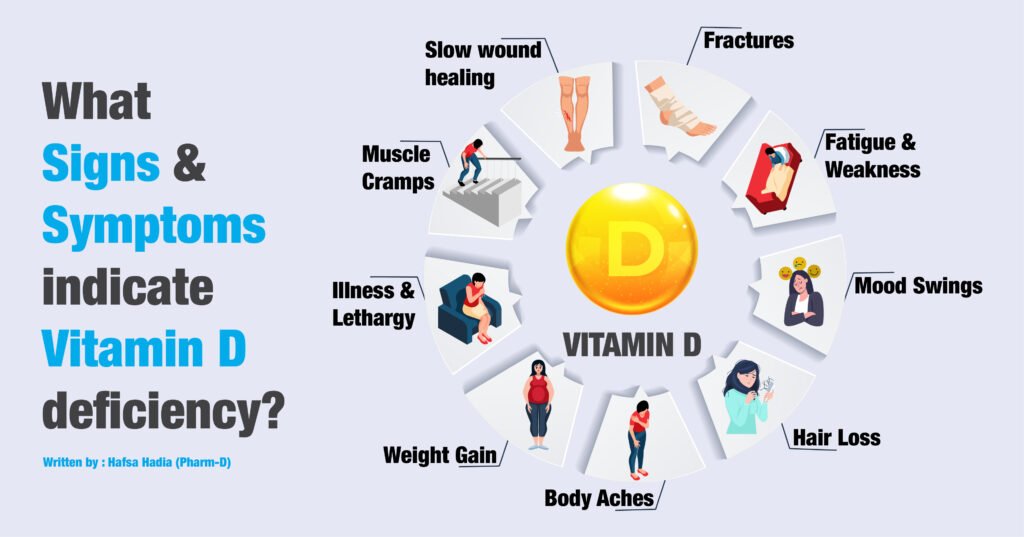
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can manifest in various ways. Here are the most common symptoms to watch out for:
1. Frequent Illness or Infections
Vitamin D plays a key role in immune function, and low levels of this vitamin can impair the body’s ability to fight infections. Research links deficiency to respiratory infections like colds, pneumonia, and even viral diseases like COVID-19. Regular supplementation may reduce the risk of such infections, particularly in those with very low vitamin D levels.
2. Fatigue and Tiredness
A common symptom of vitamin D deficiency is persistent fatigue. Studies have shown a correlation between low vitamin D levels and chronic tiredness, especially in older adults and children. Supplementing with vitamin D may help alleviate these symptoms and improve overall energy levels.
3. Bone and Back Pain
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, and a lack of it can result in bone pain and discomfort, particularly in the lower back. Research indicates that people with arthritis and chronic muscle pain tend to have lower vitamin D levels.
4. Anxiety and Depression
There is growing evidence suggesting a link between vitamin D deficiency and mood disorders like anxiety and depression. Although research is ongoing, some studies indicate that vitamin D supplementation may help alleviate symptoms of depression, particularly in older adults.
5. Slow Wound Healing
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the wound healing process. A deficiency may slow down recovery after surgery or injury. It enhances the production of compounds vital for forming new skin and tissue, and its role in inflammation management is also essential for proper healing.
6. Bone Loss
Low vitamin D levels can lead to bone mineral density loss, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis. It’s especially important for older adults and postmenopausal women, as they are more susceptible to bone-related issues due to reduced calcium absorption.
7. Hair Loss
Hair loss, especially in cases like alopecia areata, has been linked to vitamin D deficiency. Some studies suggest that increasing vitamin D levels can help promote hair regrowth, particularly when applied topically or taken as supplements.
8. Muscle Pain
Low vitamin D levels are associated with muscle pain, particularly chronic pain. Vitamin D may play a role in the body’s pain pathways, and supplementation has shown promise in reducing pain in people with vitamin D deficiency.
9. Weight Gain
Research suggests that there may be a connection between low vitamin D levels and weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. Though more studies are needed, there’s evidence indicating that maintaining healthy vitamin D levels may help manage weight.
Risk Factors for Vitamin D Deficiency

Several factors can increase the risk of developing a vitamin D deficiency:
- Darker Skin: Higher melanin levels in the skin reduce the body’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight.
- Age: Adults over 65 are at a higher risk due to changes in skin, kidneys, and liver function, which affect vitamin D production.
- Limited Sun Exposure: People who live in areas with little sunlight or who spend most of their time indoors may not get enough vitamin D.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can sequester vitamin D, making it less available to the body.
- Certain Health Conditions: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and chronic kidney or liver disease can impair nutrient absorption.
- Medications: Some medications, including statins and anticonvulsants, can interfere with vitamin D metabolism.
How to Treat Vitamin D Deficiency
Treating vitamin D deficiency typically involves:
1. Vitamin D Supplements
Supplements are the most common way to treat vitamin D deficiency. Over-the-counter options like cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) are widely available. For severe deficiencies, a doctor may prescribe higher doses, up to 50,000 IU per week, or recommend vitamin D injections.
2. Magnesium Supplements
Since magnesium helps activate vitamin D in the body, supplementing with magnesium may improve the effectiveness of vitamin D therapy.
3. Vitamin D-Rich Foods
Including more vitamin D-rich foods in your diet can help boost your levels. These include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified milk and cereals
- Beef liver
- Yogurt
4. Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, and spending time outdoors, especially in the morning or late afternoon, can help your body produce more of it. However, always take precautions to avoid overexposure, such as using sunscreen and limiting your time in direct sunlight.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you have a vitamin D deficiency, consult with a healthcare provider. Symptoms can be subtle, and a blood test (25-hydroxy vitamin D test) can determine if your levels are low. Your doctor can recommend the best course of action based on your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I increase my vitamin D levels?
- Get more sunlight, take vitamin D supplements, and eat more vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish and fortified milk.
How long does it take to treat vitamin D deficiency?
- Treatment duration varies depending on the severity of the deficiency. Generally, it may take 10 weeks for adults and up to 12 weeks for children to reach optimal vitamin D levels with supplements.
Takeaway
Vitamin D deficiency is more common than you might think, and its symptoms can often be mistaken for other health issues. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, consider talking to a healthcare professional about a vitamin D test. Treatment usually involves supplements, dietary adjustments, and increased sun exposure. Early detection and treatment can help improve your overall health and prevent potential complications.